Radiology
MRI Basics
SEQUENCES
- T1
- DWI – Diffusion Weighted Imaging
- 3D SWAN – Susceptibility weighted Angiography
- PD – replaced by FLAIR
- T1 MPIR/FLAIR – Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- FIESTA-C – fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition
- T2 FSE – fast spin echo
- T2 PROPELLER – periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction AKA BLADE
- BRAVO PRE – T1w contrast between grey and white matter
- BRAVO +C
- Exponential ADC - Apparent diffusion coefficient
- Apparent ADC - Apparent diffusion coefficient
- SWAN REFROMAT

BASICS
- high signal intensity = white
- hyperintense = brighter than the thing we are comparing it to
- low signal intensity = black
- hypointense = darker than the thing we are comparing it to
- Repetition Time (TR) is the amount of time between successive pulse sequences applied to the same slice
- Time to Echo (TE) is the time between the delivery of the RF pulse and the receipt of the echo signal
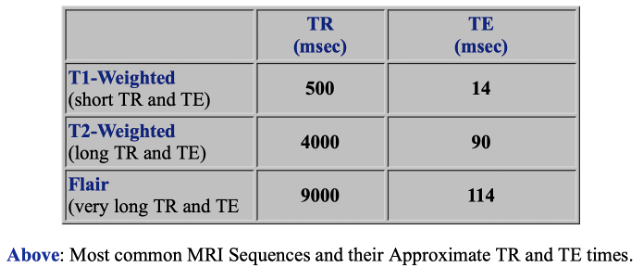
T1-Sequences
- assess basic anatomy. Sagittal = money shot
- CSF = DARK on T1-weighted imaging
- White matter = light, Cortex (aka gray matter) = gray
T2-Sequences
- if bright spot in sinus = sinus clot
- CSF = BRIGHT on T2-weighted imaging
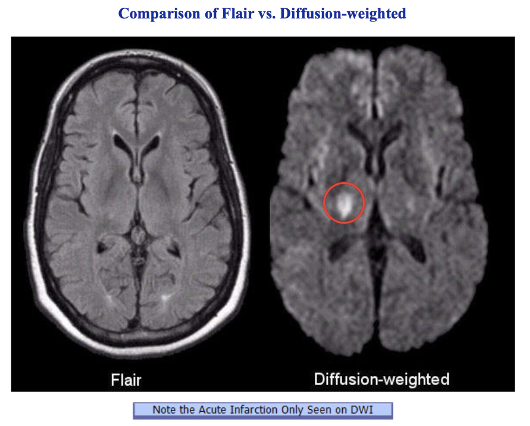
FLAIR aka T1 MPIR/FLAIR - Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- abnormalities remain bright but normal CSF fluid is attenuated and made dark. This sequence is very sensitive to pathology and makes the differentiation between CSF and an abnormality much easier.
- Inflammation (infection, demyelination) = BRIGHT

DWI (Diffusion weighted imaging)
- detect the random movements of water protons and gives insight into cellularity (tumors), cell swelling (ischemia) and edema
- Water molecules diffuse relatively freely in the extracellular space; their movement is significantly restricted in the intracellular space. Spontaneous movements, referred to as diffusion, rapidly become restricted in ischemic brain tissue. During ischemia, the Na-K pump shuts down and sodium accumulates intracellularly. Water then shifts from the extracellular to the intracellular space due to the osmotic gradient. As water movement becomes restricted intracellularly, this results in an extremely bright signal on DWI.
- Acute pathology (ischemic stroke, cellular tumor, pus) = increased signal denoting restricted diffusion
- T2 shine through = because component of the image is derived from T2 signal, some tissues that are bright on T2 will appear bright on DWI images without there being an abnormal restricted diffusion.
- DWI is an extremely sensitive method for detecting acute stroke.
- Look for BRIGHT spots
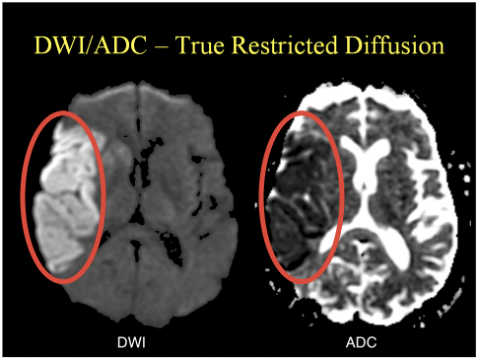
ADC (Apparent diffusion coefficient)
- representing the actual diffusion values of the tissue without T2 effects.
- Acute pathology (ischemic stroke, cellular tumor, pus) usually appears as decreased signal denoting restricted diffusion.
- appear basically as grayscale inverted DWI images
- look for dark spots (corresponding to bright spots on DWI)
 |  |
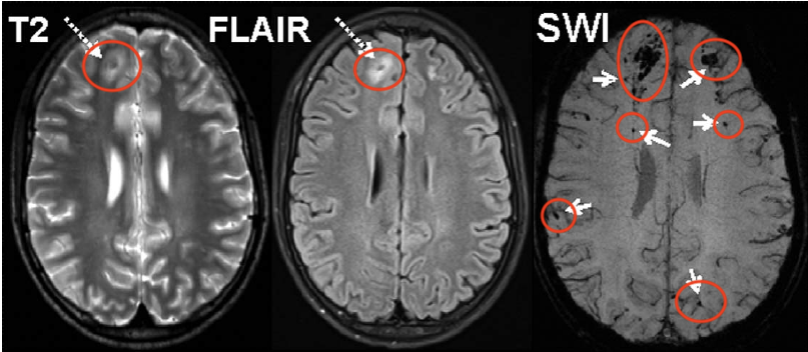
SWAN (Susceptibility-weighted angiography) aka SWI (Susceptibility Weighted Imaging)
- look for bleed aka DARK locations
ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling)
- useful for migraine, seizure, stroke evaluation
- look for areas of hyperperfusion (BRIGHT) or hypoperfusion (DARK) areas
 |
|
Post-Contrast Study
- evaluate vasculature


Vasogenic Edema VS. Cytotoxic Edema

